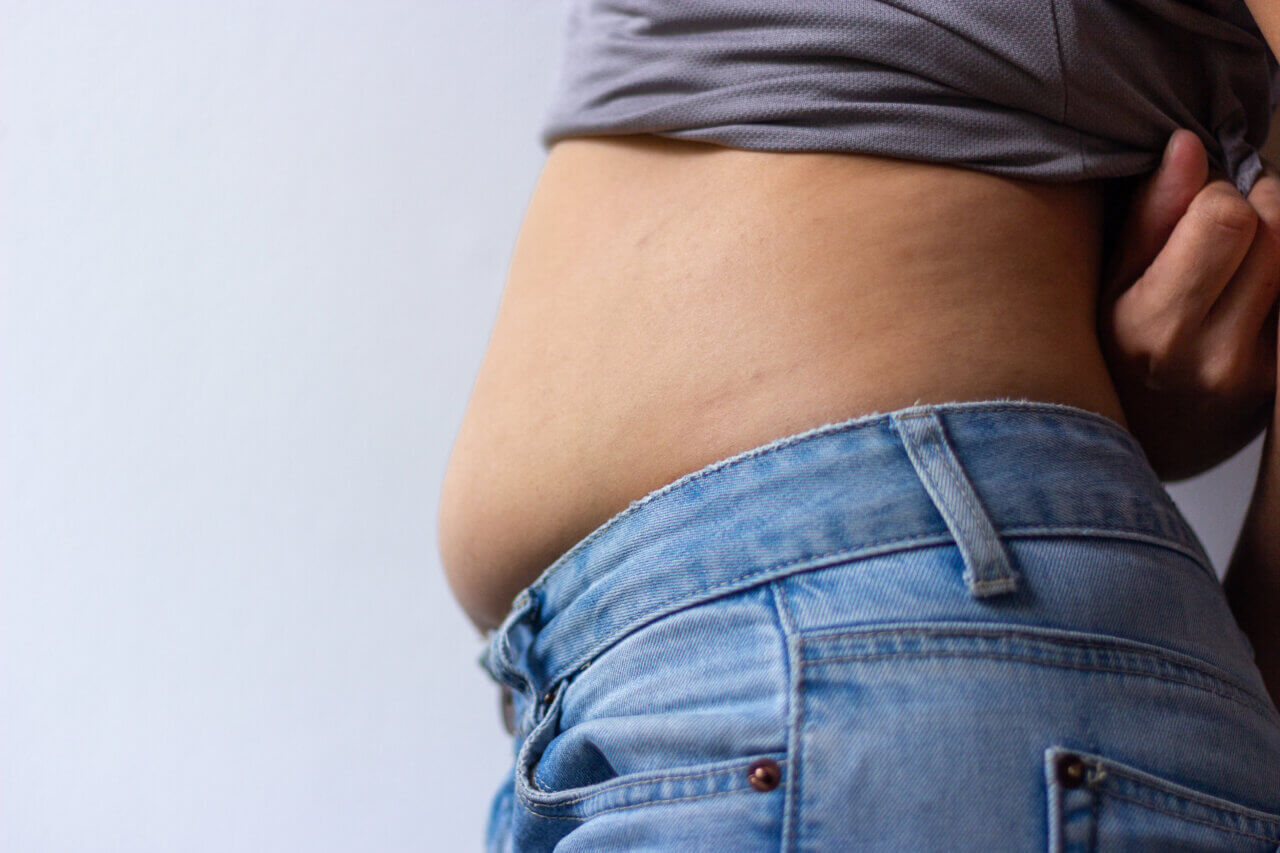
Have you ever felt your stomach feeling unusually swollen or heavy? If so, you’re not alone—bloating is a common issue that many people experience. Bloating is characterized by a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, often accompanied by gas, burping, or stomach gurgling.
What Causes Bloating?
Bloating can be triggered by a variety of factors, ranging from dietary choices to underlying digestive issues. Some of the most common causes include:
Eating Habits: Consuming fatty foods, drinking carbonated beverages, or eating too quickly can lead to bloating. These habits often cause you to swallow excess air or slow down digestion, both of which contribute to that uncomfortable bloated feeling.
Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as constipation or food intolerances, like lactose intolerance, are significant contributors to bloating. When your digestive system struggles to process certain foods, it can lead to gas buildup and bloating.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly in women during menstruation, can cause bloating. Hormonal shifts can affect how your body retains water and processes food, leading to temporary bloating.
Imbalanced Gut Bacteria: An imbalance in the gut micro biome, the community of bacteria in your digestive system, can also contribute to bloating. A lack of beneficial bacteria can slow digestion and lead to increased gas production.
Foods That Can Cause Bloating
Certain foods are more likely to cause bloating, especially those that are difficult to digest or that produce gas during digestion. Some common culprits include:
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and other legumes are rich in fiber, which can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to gas and bloating.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are known for causing bloating due to their high fiber content and the presence of raffinose, a complex sugar that can be tough to digest.
Onions and Garlic: These vegetables contain fructans, a type of carbohydrate that can cause gas and bloating in some individuals.
Dairy Products: For those who are lactose intolerant, dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt can lead to bloating, as the body struggles to break down lactose, a sugar found in milk.
Artificial Sweeteners: Sweeteners such as sorbitol and xylitol, commonly found in sugar-free products, can cause bloating because they are not fully absorbed by the body and ferment in the gut.
How to Prevent Bloating
While bloating can be uncomfortable, there are several strategies you can adopt to reduce or prevent it:
Eat Slowly: Taking your time to eat and chewing your food thoroughly can help prevent swallowing excess air, which can contribute to bloating.
Monitor Your Diet: Keeping a food diary can help you identify which foods trigger your bloating. Once identified, you can adjust your diet accordingly.
Limit Carbonated Drinks: Carbonated beverages like soda and sparkling water can introduce extra gas into your digestive system, leading to bloating.
Stay Active: Regular physical activity can aid digestion and help prevent constipation, a common cause of bloating.
Consider Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can improve digestion and reduce bloating.
If your bloating persists or worsens, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent bloating could be a sign of a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Bloating can be frustrating, but by making mindful changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can manage it more effectively. Have you ever dealt with bloating? Feel free to share what worked for you in managing this common issue.
Have you ever felt your stomach feeling unusually swollen or heavy? If so, you’re not alone—bloating is a common issue that many people experience. Bloating is characterized by a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, often accompanied by gas, burping, or stomach gurgling.
What Causes Bloating?
Bloating can be triggered by a variety of factors, ranging from dietary choices to underlying digestive issues. Some of the most common causes include:
Eating Habits: Consuming fatty foods, drinking carbonated beverages, or eating too quickly can lead to bloating. These habits often cause you to swallow excess air or slow down digestion, both of which contribute to that uncomfortable bloated feeling.
Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as constipation or food intolerances, like lactose intolerance, are significant contributors to bloating. When your digestive system struggles to process certain foods, it can lead to gas buildup and bloating.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly in women during menstruation, can cause bloating. Hormonal shifts can affect how your body retains water and processes food, leading to temporary bloating.
Imbalanced Gut Bacteria: An imbalance in the gut micro biome, the community of bacteria in your digestive system, can also contribute to bloating. A lack of beneficial bacteria can slow digestion and lead to increased gas production.
Foods That Can Cause Bloating
Certain foods are more likely to cause bloating, especially those that are difficult to digest or that produce gas during digestion. Some common culprits include:
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and other legumes are rich in fiber, which can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to gas and bloating.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are known for causing bloating due to their high fiber content and the presence of raffinose, a complex sugar that can be tough to digest.
Onions and Garlic: These vegetables contain fructans, a type of carbohydrate that can cause gas and bloating in some individuals.
Dairy Products: For those who are lactose intolerant, dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt can lead to bloating, as the body struggles to break down lactose, a sugar found in milk.
Artificial Sweeteners: Sweeteners such as sorbitol and xylitol, commonly found in sugar-free products, can cause bloating because they are not fully absorbed by the body and ferment in the gut.
How to Prevent Bloating
While bloating can be uncomfortable, there are several strategies you can adopt to reduce or prevent it:
Eat Slowly: Taking your time to eat and chewing your food thoroughly can help prevent swallowing excess air, which can contribute to bloating.
Monitor Your Diet: Keeping a food diary can help you identify which foods trigger your bloating. Once identified, you can adjust your diet accordingly.
Limit Carbonated Drinks: Carbonated beverages like soda and sparkling water can introduce extra gas into your digestive system, leading to bloating.
Stay Active: Regular physical activity can aid digestion and help prevent constipation, a common cause of bloating.
Consider Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can improve digestion and reduce bloating.
If your bloating persists or worsens, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent bloating could be a sign of a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Bloating can be frustrating, but by making mindful changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can manage it more effectively. Have you ever dealt with bloating? Feel free to share what worked for you in managing this common issue.